Chill Room: Pocket Edition
Client
Allegheny Health Network
Role
Year
2025
Team
Project Manager, Engineer, Artist
Context
I helped build this mobile app for iOS and Android in partnership with Allegheny Health Network's Chill Project. The mission is to equip middle school students with the tools they need to navigate their emotions and strengthen their ability to identify, discuss, and react to stress with resilience. Recognizing that access to traditional "Chill Rooms" and similar stress management programs in schools is not always available, we've designed a mobile app that brings some of the Chill Room's essential support resources directly to students, offering consistent access to strategies for managing stress and fostering self-awareness.
Transformational Goals
- Knowledge: Players deepen their understanding of resilience, self-awareness, and effective coping mechanisms.
- Experience: Players are guided to a digital "oasis" for a self-regulation break when it makes sense and is safe-enough to do so.
- Behavior: Players build skills to recognize and respond to stress triggers more effectively.
The Gameplay Loop
The game's loop embeds our transformational goals within the play of the game. The scope and sequence of the curriculum were determined in consultation with subject matter experts to focus on foundational emotional awareness skills.
Step 1: Check In & Collect
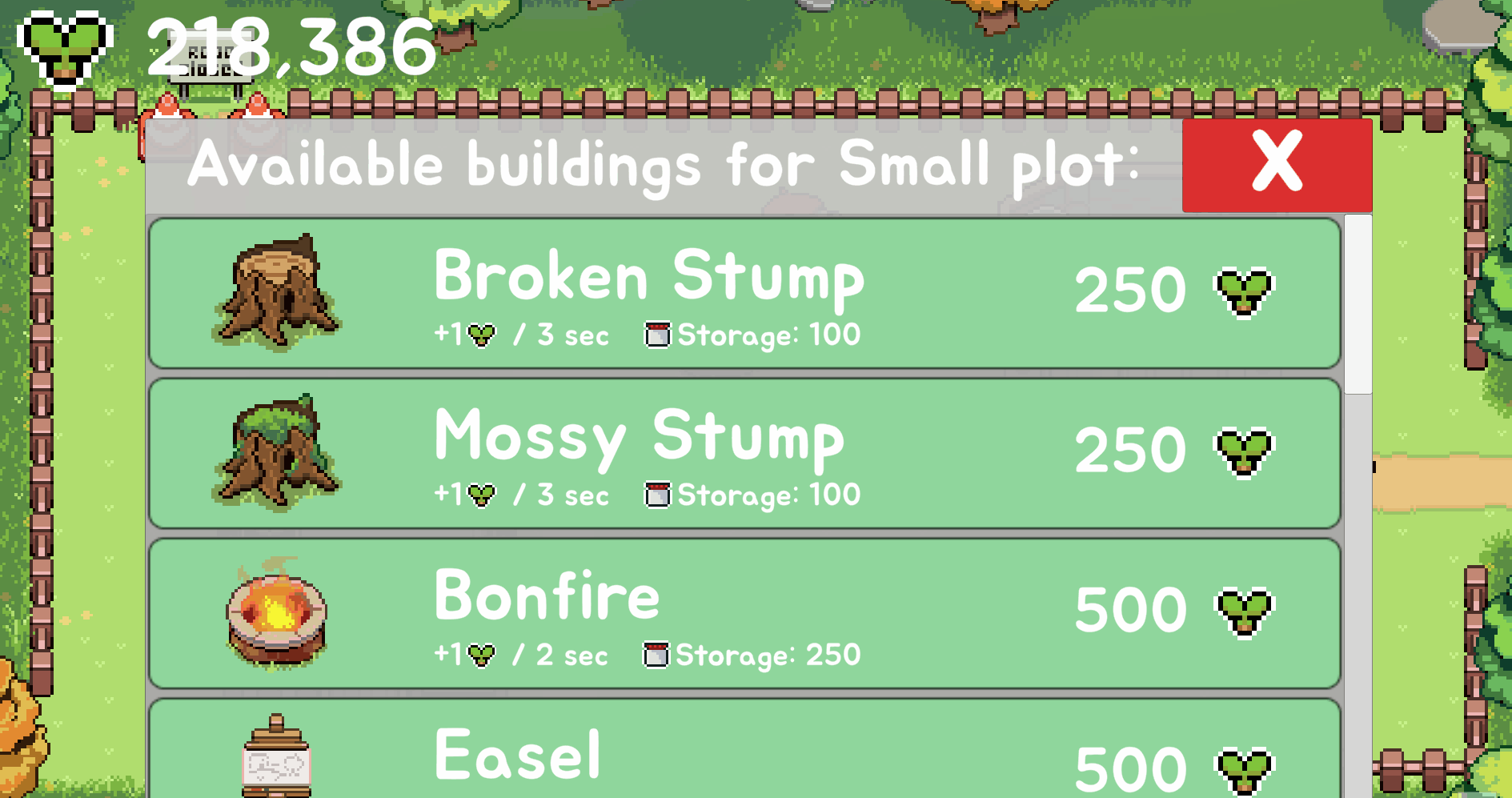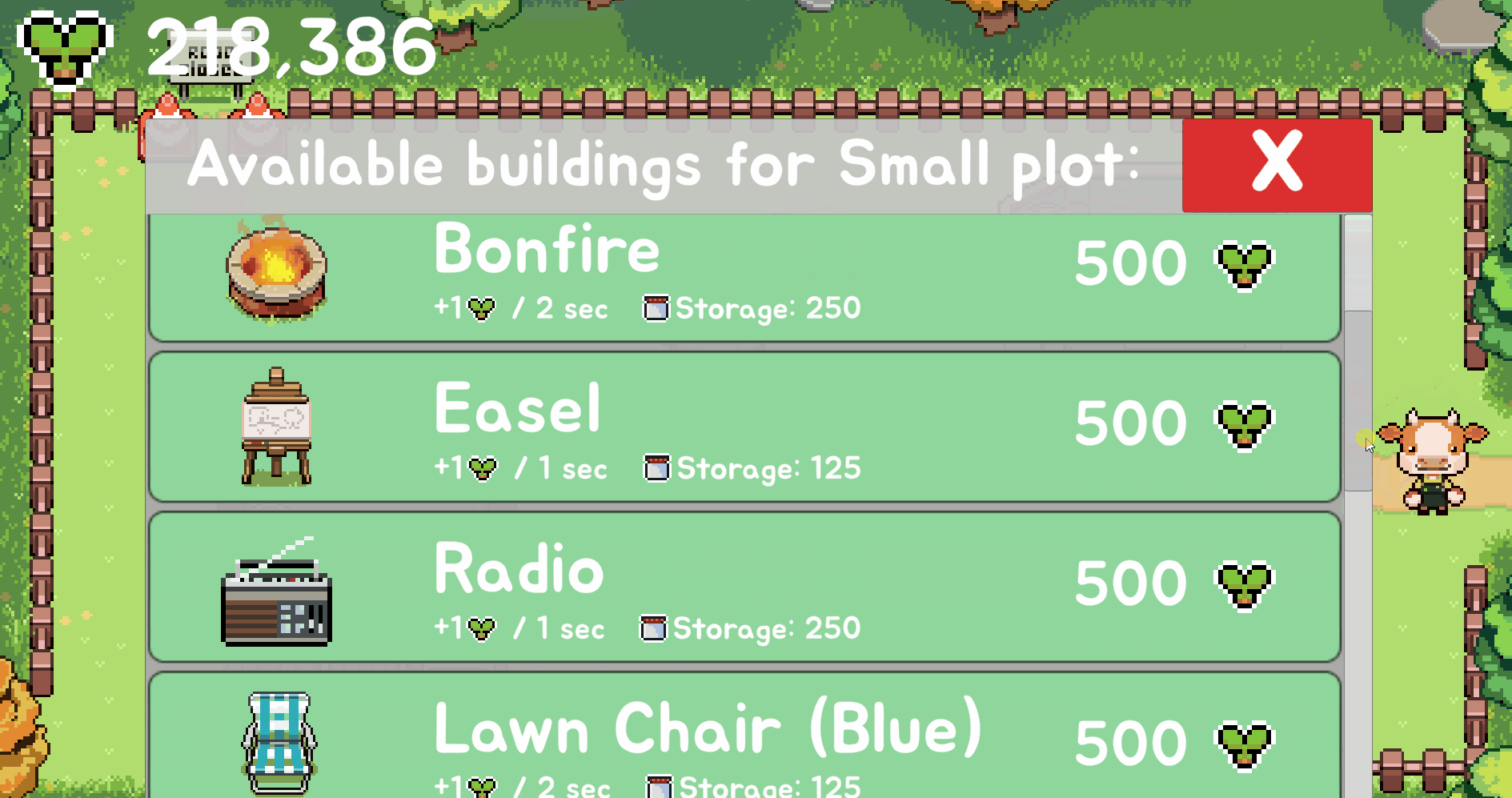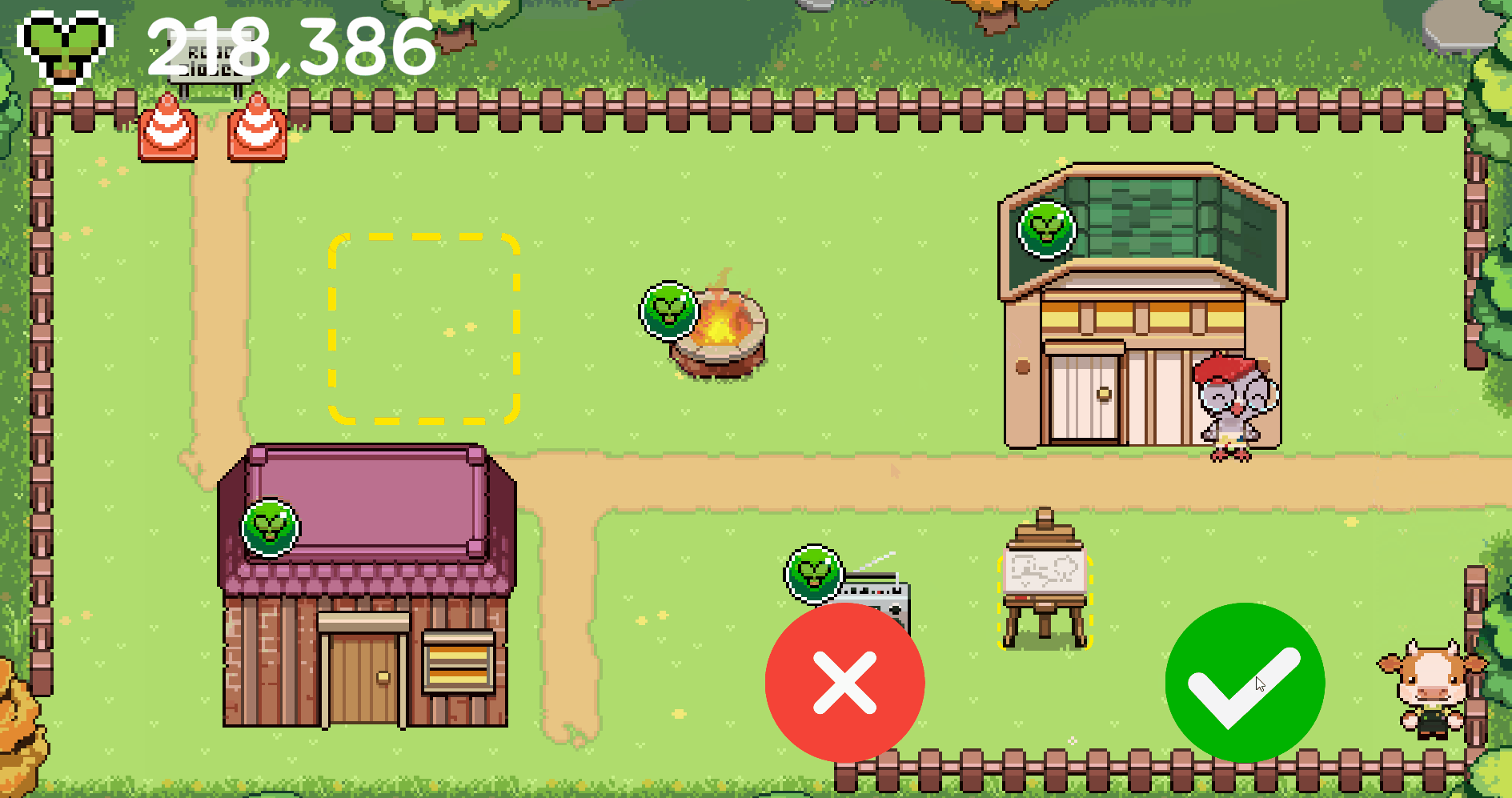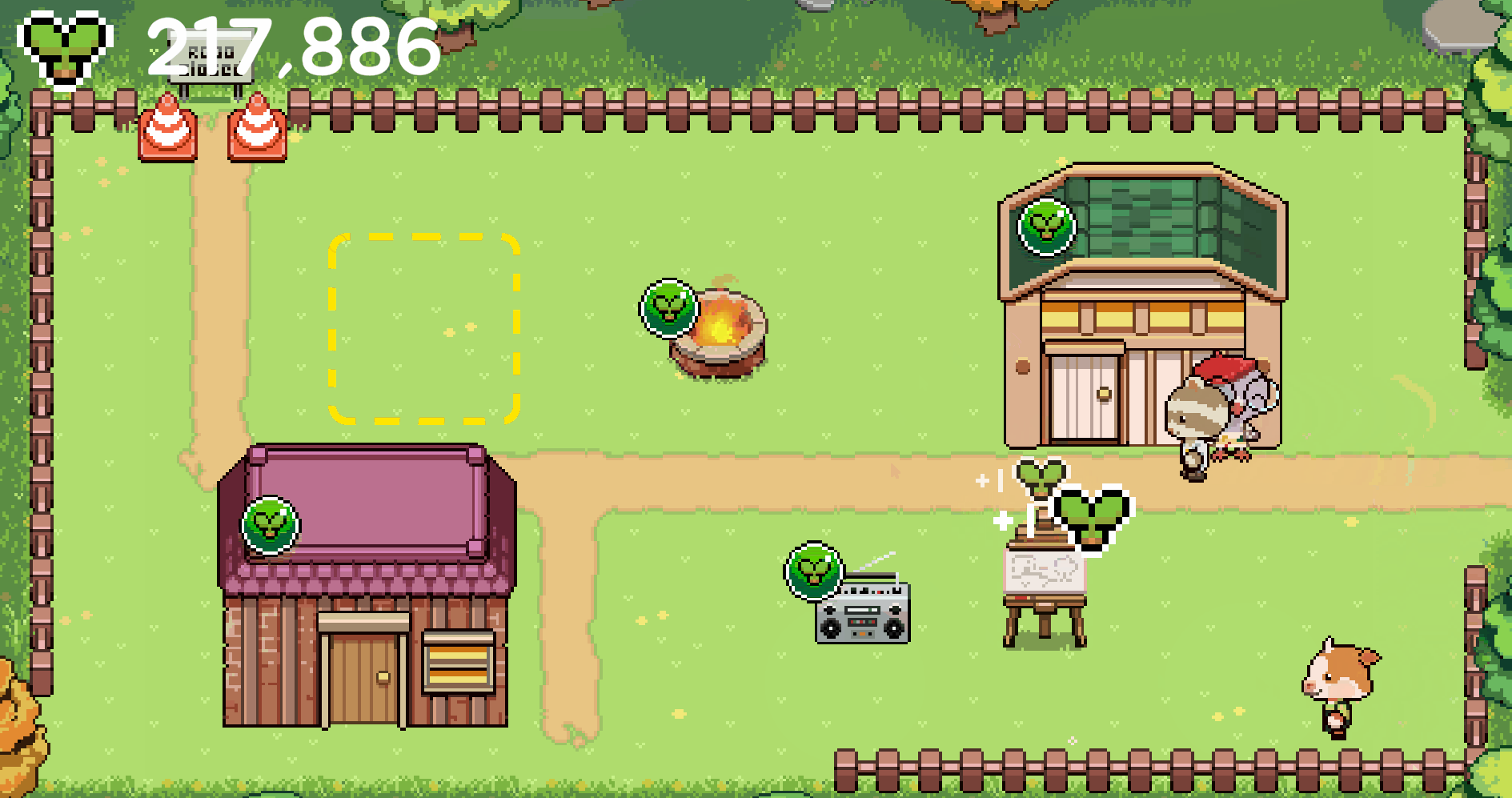
The player opens the app to their village. Through idle mechanics, structures have passively generated "Harvest," the game's currency. The player is immediately rewarded for returning by collecting these resources from buildings, surprise boxes, or interactive elements like butterflies.

Step 2: Access the Village
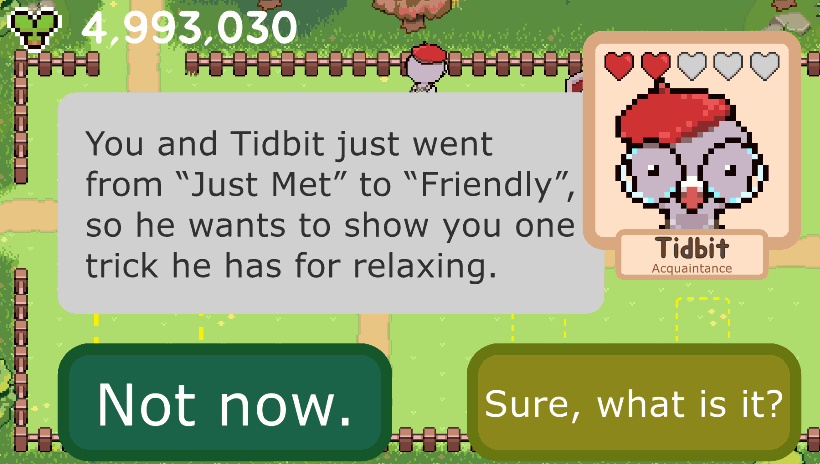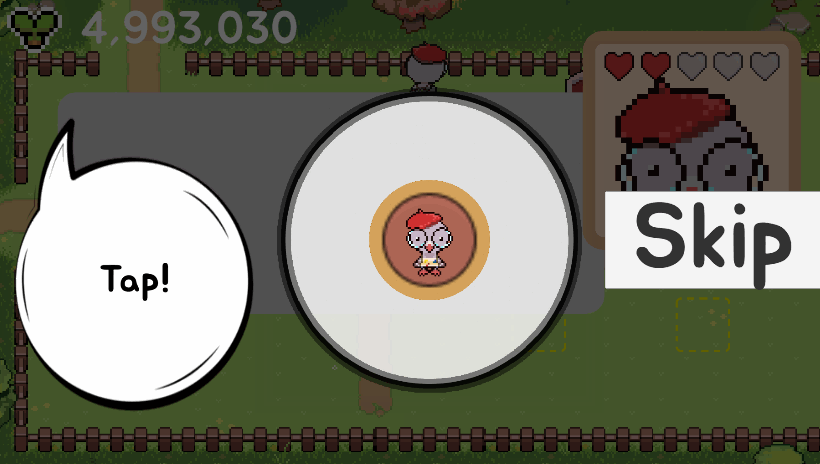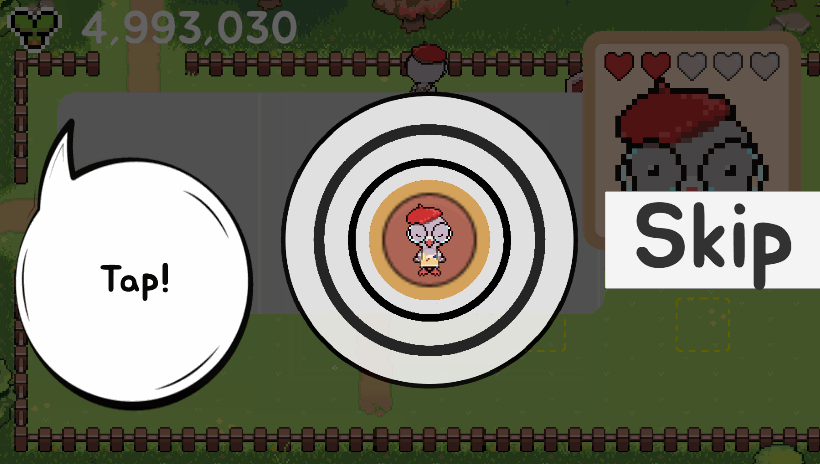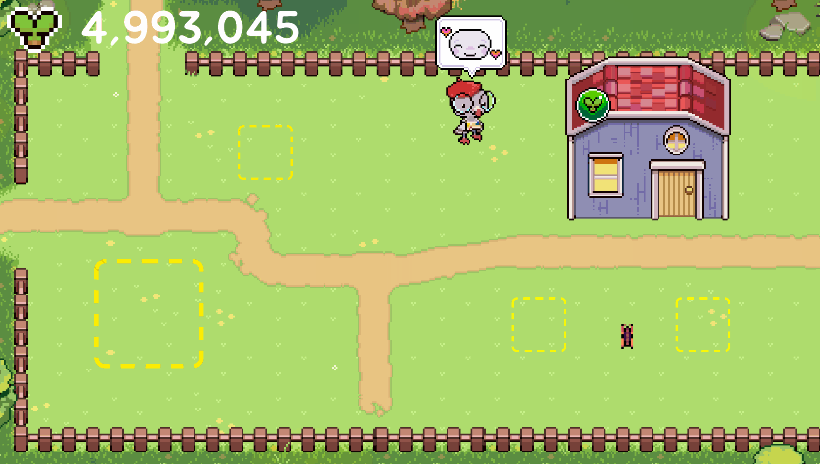
The player observes their villagers. Some are happy, but occasionally, a villager will be in a "bad mood," indicated by a cloud over their head. This state is a core part of the transformational design.

Step 3: Interact & Learn
The player taps a villager to start a conversation. The learning design follows a structured two-phase approach. First, in Exposure phases, villagers introduce concepts (in the prototype, this is about naming & recognizing the feel of the six basic emotions) in low-stakes dialogues. Then, in Knowledge Check phases, players must apply that knowledge to help a villager, reinforcing learning through retrieval practice. Content reappears using a technique called Spaced Repetition shown to aid memory recall.

Step 4: Practice a Skill
Certain dialogues trigger a rhythm-based deep breathing exercise. The player participates by tapping the screen in time with the visual cues, helping a villager calm down while practicing a tangible self-regulation skill themselves. Although deep breathing is the only "procedural skill" in the prototype, this same minigame can be expanded to show the steps of any self-regulation skill, such as color spotting, mindful walking, and other CBT skills that have multiple steps.
Step 5: Grow & Build
Using the collected "Harvest," the player buys new structures, upgrades existing ones, and personalizes their village. This tangible progress, and visible improvement and deepending of their relationships to villagers, are the rewards for their engagement and support.
Playtesting Shapes the Design
A prototype's true value is in what it teaches us. Through playtesting, we identify what isn't working and adapt our design to better serve our players and our transformational goals.
While we have made too many changes informed by playtesting to list them all here, below are three of the most recent key changes we're making based on direct player feedback.
Deepening Curriculum Engagement
The Observation: We saw that players, while enjoying the swipe mechanic, often chose answers randomly without deeply engaging with the curriculum content in dialogues.
Key Insight: The format in which answers were hidden and required swiping left and right to reference them, and some of the dialogue did not have reward stakes while other dialogue did-- was encouraging guessing over learning. We needed to introduce concepts more gently and make the choice interface more deliberate.
Iterations:
- Introducing "Sensitizing Exposure": Concepts are now introduced organically in low-stakes conversations that connect the skill to the player's own life (e.g., "When you get stressed, do you ever feel shaky?"). This primes the player for later learning.
- Redesigning the Response Interface: While the feel of swiping was popular, it created cognitive load. We are redesigning the interface to be more intuitive, allowing players to easily compare options and make more thoughtful choices.
Balancing Economy with Relationships
The Observation: Our idle economic loop was highly effective—so much so that it sometimes overshadowed the character relationships and dialog we wanted to foster. Players focused more on collecting than connecting and reflecting.
Key Insight: The two core systems—economy and relationships—were intertwined in a way that was invisible to the player. Players needed to see that relationships and game dialog were essential to progress.
Iterations:
- Raising the Stakes: Dialogue choices now have a greater and more visible impact on villager moods, encouraging players to attend more closely to the content.
- Improving Feedback: We added a clearer tutorial and more visible UI elements to show how helping a villager immediately improves the relationship and contributes to progress. We improved the UI that communicates the current Relationship level.
- Improving Dialog: Character dialog will be rewritten to make the deepening relationship arc with the player more apparent.

From Practice to Understanding
The Observation: Players could successfully complete the rhythm minigame but struggled to articulate the steps of the skill they had just performed.
Key Insight: The procedural knowledge (the 'how') wasn't translating into declarative knowledge (the 'what' and 'why'). We needed a bridge between doing and understanding.
Iterations:
- Enhancing Visuals: We are adding a more humanoid character to perform the exercises alongside the villager for clearer demonstration and making the character animations larger.
- Adding a Reflection Phase: After the minigame, a new dialogue prompt will ask the player to reflect on the skill (e.g., "What did you notice?"), helping to turn procedural knowledge into something players can articulate out loud.
- We will need further testing to validate that these changes are having the impact we want.

Foundational Research & Key Insights
The design is grounded in established research on educational games, habit formation, and self-regulation. The following insights were critical in shaping our core mechanics and transformational goals.
Idle Mechanics for Habit Formation
To encourage the consistent, low-stress practice needed for skill-building, we adopted "idle" or "clicker" game mechanics. Research shows these systems are highly effective at motivating players to return for short, regular sessions, which is ideal for learning and habit formation.
Alexandrovsky, et al. (2019)
Embedded Design for Engagement
Games that are explicitly "for learning" can be less effective. We followed the principle of "embedded design," intermixing curriculum content with off-topic conversations and activities. This makes the learning feel more natural and intrinsically motivated.
Kaufman & Flanagan (2015)
The Power of Playing the Expert
Games allow players to try on new identities. By casting the player as an "expert" caretaker who helps villagers, we empower them to identify as someone skilled in self-regulation, which can shift their own self-perception and confidence.
Lee & Hammer (2011)
Learning by Watching (Vicarious Learning)
Watching game characters model skills can be a powerful teaching tool. Our rhythm mini-games, where villagers demonstrate breathing exercises, are based on research showing that observing and then mimicking behavior is highly effective for skill acquisition.
Nørlev, et al. (2022)

